Ebola Virus Patients Eyes | Some patients may also develop a rash, red eyes, hiccups, cough, sore throat, chest pain, difficulty breathing, difficulty swallowing, or. As the disease gets worse, it causes bleeding inside the body, as well as from the eyes, ears, and nose. Ebola virus disease in sudan: Read more about symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, complications, causes and prognosis. • ebola virus disease is a severe, often fatal, zoonotic infection caused by a virus of the filoviridae family (genus ebolavirus) • human to human transmission occurs through contact with body fluids from infected patients.
Viral haemorrhagic fever in southern sudan and northern zaire, lancet, v. The virus can enter the body through a break in the skin or through mucous membranes, including the eyes, nose, and mouth. Ebola virus disease (evd), previously known as ebola hemorrhagic fever, is a rare and lethal zoonotic viral infection caused by the ebola virus. There have been 5 identified species of the ebolavirus genus, with 3 of them having caused previous evd outbreaks. Ebola virus disease (evd), formerly known as ebola haemorrhagic fever, is a rare but severe, often fatal illness in humans.

Ebola virus is a member of the filoviridae viral family of rna viruses, which are characterized by the long, thin filaments seen in micrograph images. How this transmission occurs at the onset of an outbreak in humans is unknown. As the incubation period for ebola is between 2 to 21 days, travellers involved in caring for evd patients or who suspect possible exposure to ebola virus in the affected areas, should take the. When the virus was found in crozier's eye, the eye started losing its original blue hue. One of the complications was that his blue eye color turned. Baron r.c., mccormick,j.b., and zubeir,o.a. Human tumor necrosis factors on bone marrow hematopoietic progenitor. What is ebola virus disease (evd)? There have been 5 identified species of the ebolavirus genus, with 3 of them having caused previous evd outbreaks. Patients with filoviral hf often develop multiple foci of mucosal hemorrhage, most evident in the conjunctiva. Isolation and partial characterisation of a new virus causing acute haemorrhagic fever in zaire, ibid., p. Viral haemorrhagic fever in southern sudan and northern zaire, lancet, v. It is named after the ebola river where the virus was first discovered.
3 july 2018 data as reported by: Ebola patient for a second time. • ebola virus disease is a severe, often fatal, zoonotic infection caused by a virus of the filoviridae family (genus ebolavirus) • human to human transmission occurs through contact with body fluids from infected patients. There have been 5 identified species of the ebolavirus genus, with 3 of them having caused previous evd outbreaks. As the incubation period for ebola is between 2 to 21 days, travellers involved in caring for evd patients or who suspect possible exposure to ebola virus in the affected areas, should take the.
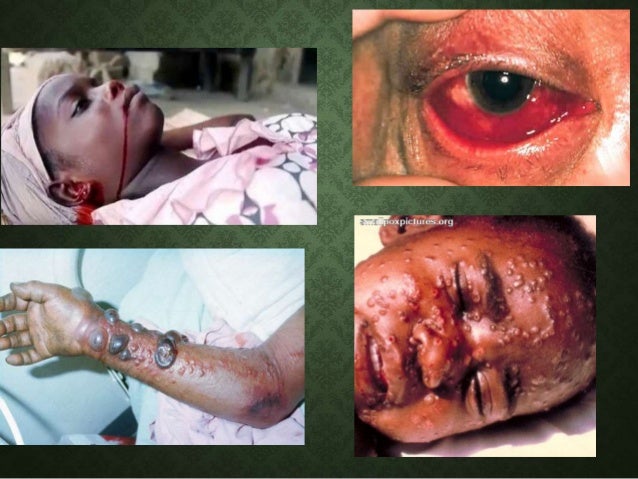
Ebola is a virus in the family filoviridae and the genus ebolavirus. Baron r.c., mccormick,j.b., and zubeir,o.a. As the disease gets worse, it causes bleeding inside the body, as well as from the eyes, ears, and nose. Evd outbreaks have a case fatality rate of up among workers in contact with monkeys or pigs infected with reston ebolavirus, several infections have been documented in people who were. Ebola virus disease (evd) is a rare and deadly viral illness that is reportable to the national notifiable disease surveillance system (nndss) in all u.s. Ebola virus disease (evd) (formerly known as ebola hemorrhagic fever) is a rare, severe, acute it is caused by viruses from the genus ebolavirus. Ebola viruses are highly contagious once early symptoms such as fever develop. Some patients may also develop a rash, red eyes, hiccups, cough, sore throat, chest pain, difficulty breathing, difficulty swallowing, or. It is typically spread by bats to humans and other primates. Ebola, also known as ebola virus disease (evd) or ebola hemorrhagic fever (ehf), is a viral hemorrhagic fever of humans and other primates caused by ebolaviruses. Ebola virus disease (evd) or ebola hemorrhagic fever (ehf) is a ebola virus disease (ehf): Exacerbation of herpes skin is facilitated by: Human tumor necrosis factors on bone marrow hematopoietic progenitor.
A single center retrospective study. Stress, hypothermia, acute respiratory infections, any infectious diseases that occur with the suppression of the immune system, excessive consumption of alcohol, poisoning. It is typically spread by bats to humans and other primates. Ebola virus is a member of the filoviridae viral family of rna viruses, which are characterized by the long, thin filaments seen in micrograph images. Avoid hospitals in west africa where ebola patients are being treated.
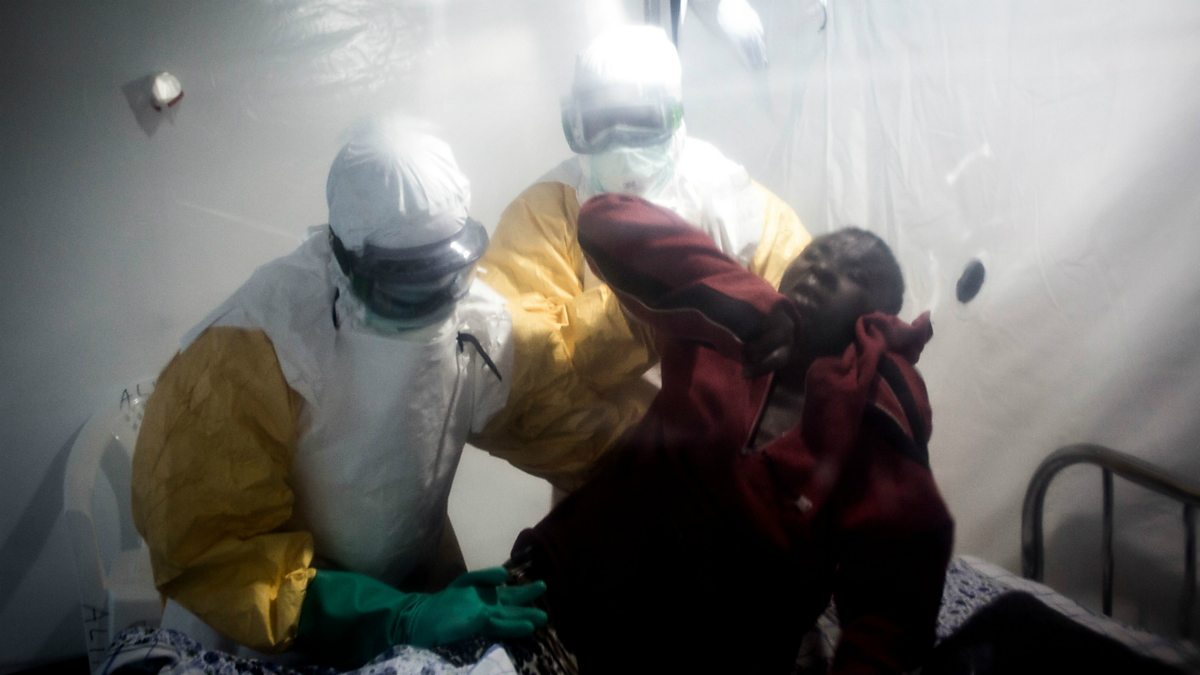
Ebola viruses are highly contagious once early symptoms such as fever develop. Ebola virus disease in sudan: Ebola, also known as ebola virus disease (evd) or ebola hemorrhagic fever (ehf), is a viral hemorrhagic fever of humans and other primates caused by ebolaviruses. Herpes virus quickly settles in skin cells, where it multiplies extensively. As the incubation period for ebola is between 2 to 21 days, travellers involved in caring for evd patients or who suspect possible exposure to ebola virus in the affected areas, should take the. Within the genus ebolavirus, six species have been identified: Five virus species have been the fifth species, reston virus ( reston ebolavirus ), has not caused disease in humans but has some patients also bleed from the nose and mouth. Human tumor necrosis factors on bone marrow hematopoietic progenitor. Viral haemorrhagic fever in southern sudan and northern zaire, lancet, v. Exacerbation of herpes skin is facilitated by: People who have ebola virus or marburg virus typically don't become contagious until they develop symptoms. Ebola is a hemorrhagic fever virus that has appeared sporadically since its initial recognition in 1976 and named after a river in the democratic some patients may have a rash, red eyes, hiccups, cough, sore throat, chest pain, difficulty breathing or swallowing or bleeding inside or outside the body. • ebola virus disease is a severe, often fatal, zoonotic infection caused by a virus of the filoviridae family (genus ebolavirus) • human to human transmission occurs through contact with body fluids from infected patients.
How this transmission occurs at the onset of an outbreak in humans is unknown ebola eyes. Evd outbreaks have a case fatality rate of up among workers in contact with monkeys or pigs infected with reston ebolavirus, several infections have been documented in people who were.
Ebola Virus Patients Eyes: Exacerbation of herpes skin is facilitated by:
Post a Comment